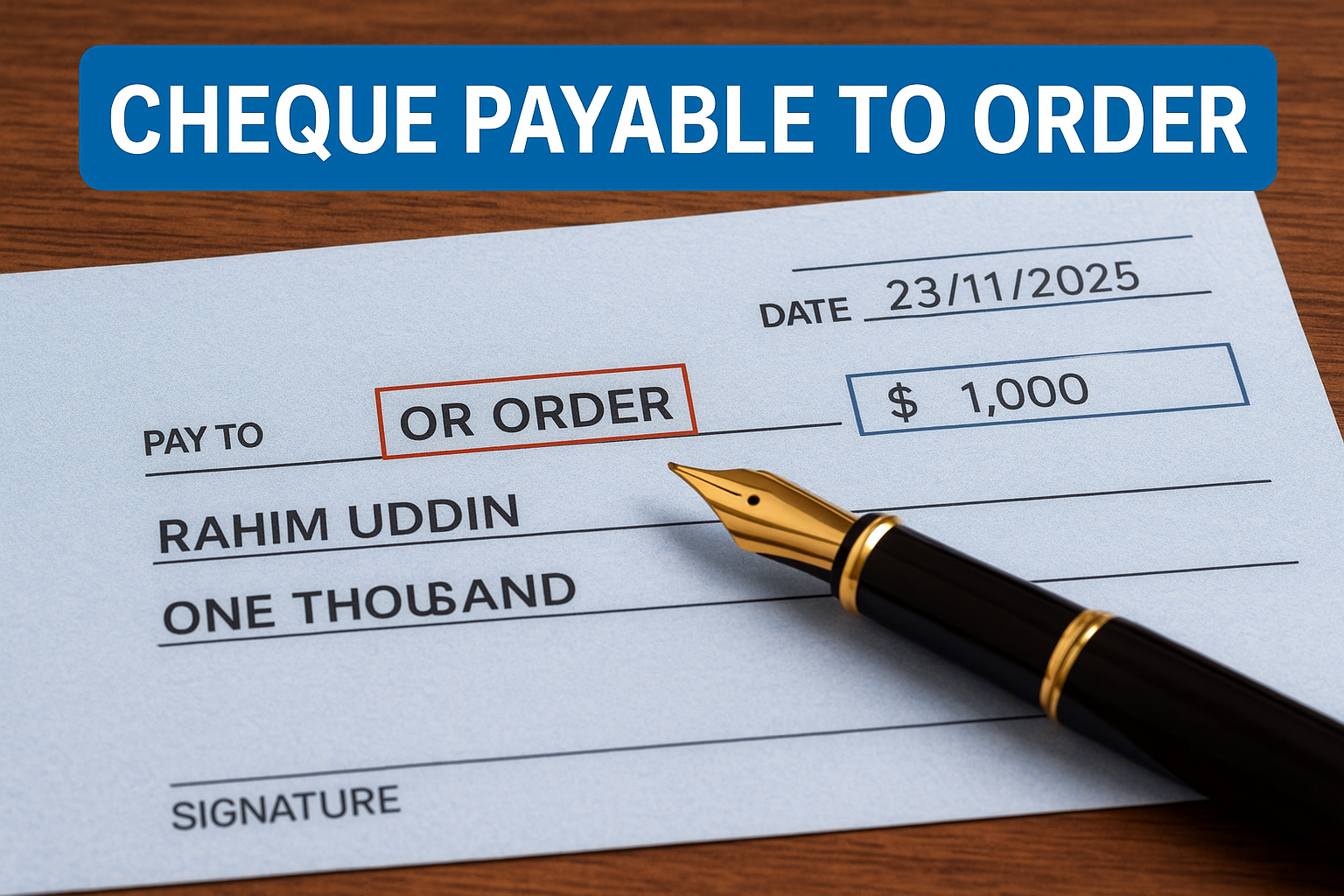
Cheque Payable to Order – Meaning, Features, Rules & Banking Examples
A cheque payable to order is one of the most secure payment instruments used in banking. It ensures
that the payment is made only to the named person or someone properly endorsed by them.
If you want to learn more about how cheques work in Bangladesh, you can also explore our detailed guide on
Cheque in Bangladesh: Definition, Types & Rules
.
What Is a Cheque Payable to Order?
A cheque payable to order—also known simply as an order cheque—is payable only to:
- The person whose name is written as the payee, OR
- The person to whom the payee legally endorses the cheque.
This makes it more secure than a bearer cheque, where anyone holding the cheque can withdraw money.
Legal Basis Under the Negotiable Instruments Act
Order cheques are governed by the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881.
Even if the words “or order” are not mentioned, a cheque is treated as an order cheque unless it explicitly states “bearer.”
To understand related concepts such as holder rights, you may check:
Holder in Due Course (HDC) – Definition & Rights
.
For the official legal text, visit the government portal:
Bangladesh Law Portal – NI Act.
How to Identify an Order Cheque
Common indicators include:
- The payee’s name is clearly mentioned
- The cheque does not include “bearer” after the name
- The cheque may include the phrase “or order” (optional)
Even without the words “or order,” it will still be considered an order cheque unless marked as “bearer.”
Security Features of Order Cheques
- Identity verification is required before payment
- Endorsement must be valid when transferring
- Lower risk if lost or stolen
Banks prefer order cheques for accountable financial transactions.
What Is Endorsement?
Endorsement is the process where the payee signs on the backside of the cheque to transfer
payment rights to another individual.
To understand endorsements in detail, check:
Negotiation of Negotiable Instruments – Meaning & Examples
.
“I endorse this cheque to Mr. Karim.”
(Signature of Rahim)
After endorsement, Karim becomes the legal holder.
How Banks Process an Order Cheque
When presented, banks must:
- Verify the name of the payee
- Match endorsement signatures
- Check identification documents
- Ensure the cheque has no overwriting
- Check available balance
Examples of Order Cheques
Example 1:
“Pay to Mahmud Hasan or order” – Only Mahmud or a properly endorsed person can receive payment.
Example 2:
“Pay to Karim & Co.” – Treated as an order cheque even without the words “or order.”
For a related study, see our detailed note on:
Bill of Exchange – Definition & Features
.
Difference Between Order Cheque and Bearer Cheque
| Order Cheque | Bearer Cheque |
|---|---|
| Payable to the named person only | Payable to anyone who presents the cheque |
| Identity verification required | No verification required |
| Safer and more secure | High risk if lost or stolen |
| Needs endorsement to transfer | No endorsement required |
To compare with similar financial instruments, you may also read:
Promissory Note – Definition & Framework
.
Uses of Order Cheques
- Salary payments
- Vendor payments
- Secure business transactions
- Loan disbursements
- Large and sensitive transactions
Reasons a Bank May Reject an Order Cheque
- Signature mismatch
- Incorrect or missing endorsement
- Torn or overwritten cheque
- Identity mismatch
- Insufficient funds
Summary
A cheque payable to order is a secure and legally protected negotiable instrument widely used in modern banking.
It ensures that funds reach the correct person through verification and endorsement.
If you are preparing for banking jobs, IBB exams, or working in General Banking, this knowledge is essential.
For more exam resources, visit:
IBB Exam Resources & Result Updates
.