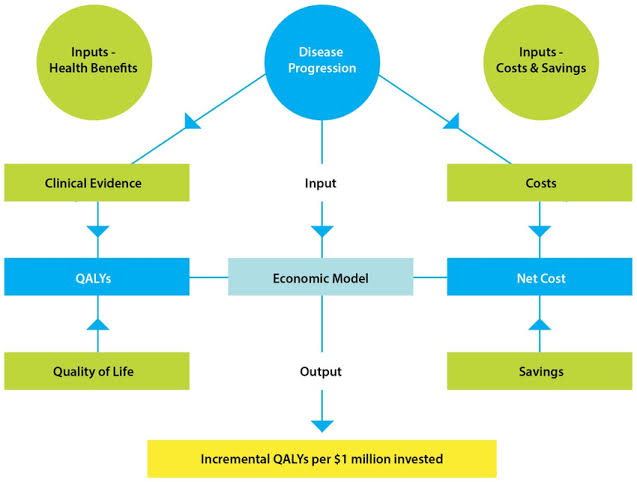
What is an Economic Model?
An economic model is a simplified representation of real-world economic processes. It helps economists analyze, explain, and predict economic behaviors by focusing on key variables while ignoring unnecessary details.
Types of Economic Models
1️⃣ Descriptive Models – Explain economic behaviors and relationships without mathematical formulations.
2️⃣ Predictive Models – Use statistical and mathematical techniques to forecast economic trends.
3️⃣ Normative Models – Provide recommendations for economic policies based on desired outcomes.
4️⃣ Static Models – Analyze an economy at a specific point in time.
5️⃣ Dynamic Models – Show how economic variables evolve over time.
Examples of Economic Models
✅ Circular Flow Model – Explains the flow of goods, services, and money between households and businesses.
✅ Supply and Demand Model – Demonstrates price determination in a competitive market.
✅ Production Possibility Curve (PPC) – Shows the trade-offs in resource allocation.
✅ IS-LM Model – Represents the interaction between interest rates and real GDP in macroeconomics.
Why Are Economic Models Important?
✔ Decision Making – Helps businesses and governments plan economic policies.
✔ Predict Market Trends – Assists in understanding inflation, employment, and GDP growth.
✔ Policy Formulation – Guides monetary and fiscal policy decisions.
Conclusion
Economic models are essential tools for understanding and managing economies. By simplifying complex realities, they provide insights that aid in policy-making and economic forecasting.