What is an Economy?
An economy refers to the system a country or region uses to produce, distribute, and consume goods and services. It includes industries, businesses, labor, and government policies that shape economic activities.
Types of Economies
✔ Market Economy – Driven by supply & demand with minimal government intervention.
✔ Command Economy – Controlled by the government, determining production & distribution.
✔ Mixed Economy – A blend of market freedom and government regulation.
✔ Traditional Economy – Based on customs, barter, and agriculture.
What is a Regulated Economy?
A regulated economy is an economic system where the government imposes rules and policies to control certain aspects of economic activities. This regulation ensures stability, fair competition, consumer protection, and social welfare.
Key Features of a Regulated Economy
✅ Government oversight on businesses & financial institutions
✅ Price control on essential goods
✅ Labor laws ensuring fair wages & working conditions
✅ Environmental regulations to prevent exploitation
Examples of Regulated Economies
- Bangladesh: Government controls fuel prices and essential goods.
- USA: Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulates financial markets.
- China: A mixed economy with heavy state influence on industries.
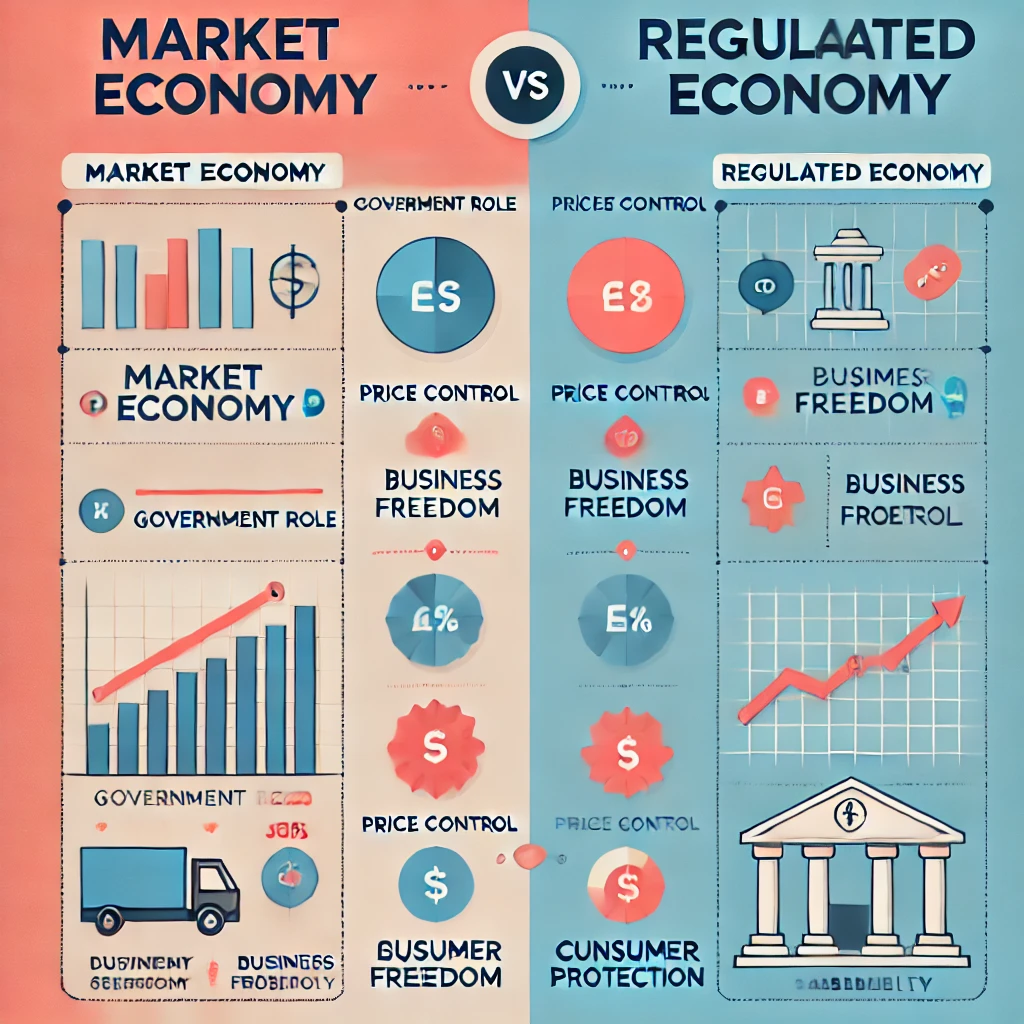
Market Economy vs. Regulated Economy
SEO-Optimized Keywords
- What is an Economy?
- Regulated Economy Explained
- Market Economy vs Regulated Economy
- Government Control in Economy
- Economic Systems Study Guide
Market Economy vs. Regulated Economy
| Feature | Market Economy | Regulated Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Government Role | Minimal | Significant |
| Price Control | Set by supply & demand | Often regulated |
| Business Freedom | High | Subject to government rules |
| Consumer Protection | Limited | Stronger regulations |
| Economic Stability | More volatile | More controlled & stable |
For more study materials, visit Banking Professional Exam Assistant.