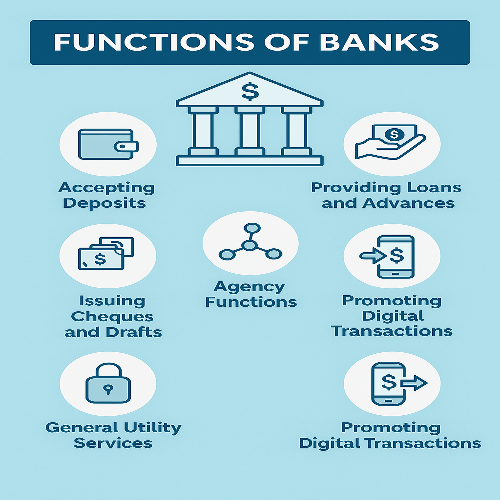
Understand the key functions of banks including deposit collection, loan disbursement, credit creation, and more that contribute to economic development.
Category: JAIBB
Types of Banks
An informative guide on different types of banks including central, commercial, cooperative, and development banks, tailored for banking professionals and students.
Understanding the Basics of Banking
Learn the basics of banking, types of bank accounts, and how banks impact the economy. A guide for individuals looking to understand financial institutions and service
Power of Attorney Act, 2012 – A Comprehensive Overview
Understand the Power of Attorney Act, 2012 in Bangladesh. Learn its features, importance, and legal impact
Environment Conservation Act, 1995
Bangladesh Environment Conservation Act, 1995 The Bangladesh Environment Conservation Act, 1995 was enacted to protect and conserve the environment, improve environmental standards, and control environmental […]